Difference between revisions of "Music Box"
(→General Resources) |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
==General Resources== | ==General Resources== | ||
*Andrew Gregory Resources | *Andrew Gregory Resources | ||
| − | **[http://media.wpi.edu/Academics/Depts/HUA/Manzo/agreg/MusicBoxISP.pdf | + | **[http://media.wpi.edu/Academics/Depts/HUA/Manzo/agreg/MusicBoxISP.pdf Paper]<br> |
| − | **[http://media.wpi.edu/Academics/Depts/HUA/Manzo/agreg/musicbox_3dprint2016.zip | + | **[http://media.wpi.edu/Academics/Depts/HUA/Manzo/agreg/musicbox_3dprint2016.zip 3D Printer File] |
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | [[Category: Advisor:Manzo]][[Category:Interactive Systems]] | + | [[Category:Featured]][[Category: Advisor:Manzo]][[Category:Interactive Systems]] |
Latest revision as of 17:57, 17 March 2016
Contents
Music Box
A music box will typically produce sounds by using a series of pegs on a surface to pluck teeth on a tuned comb. This results in the vibration of the teeth to produce sound. The most common designs will typically use a cylinder with pegs around the outside to be hit by the teeth and produce a song. The main issue with this design is that the cylinders are difficult to produce by an individual and so the song selection is usually limited to whatever the music box came with. The goal of this project is to design a music box which can be easily produced as well as have interchangeable songs which can be produced on a 3D printer.
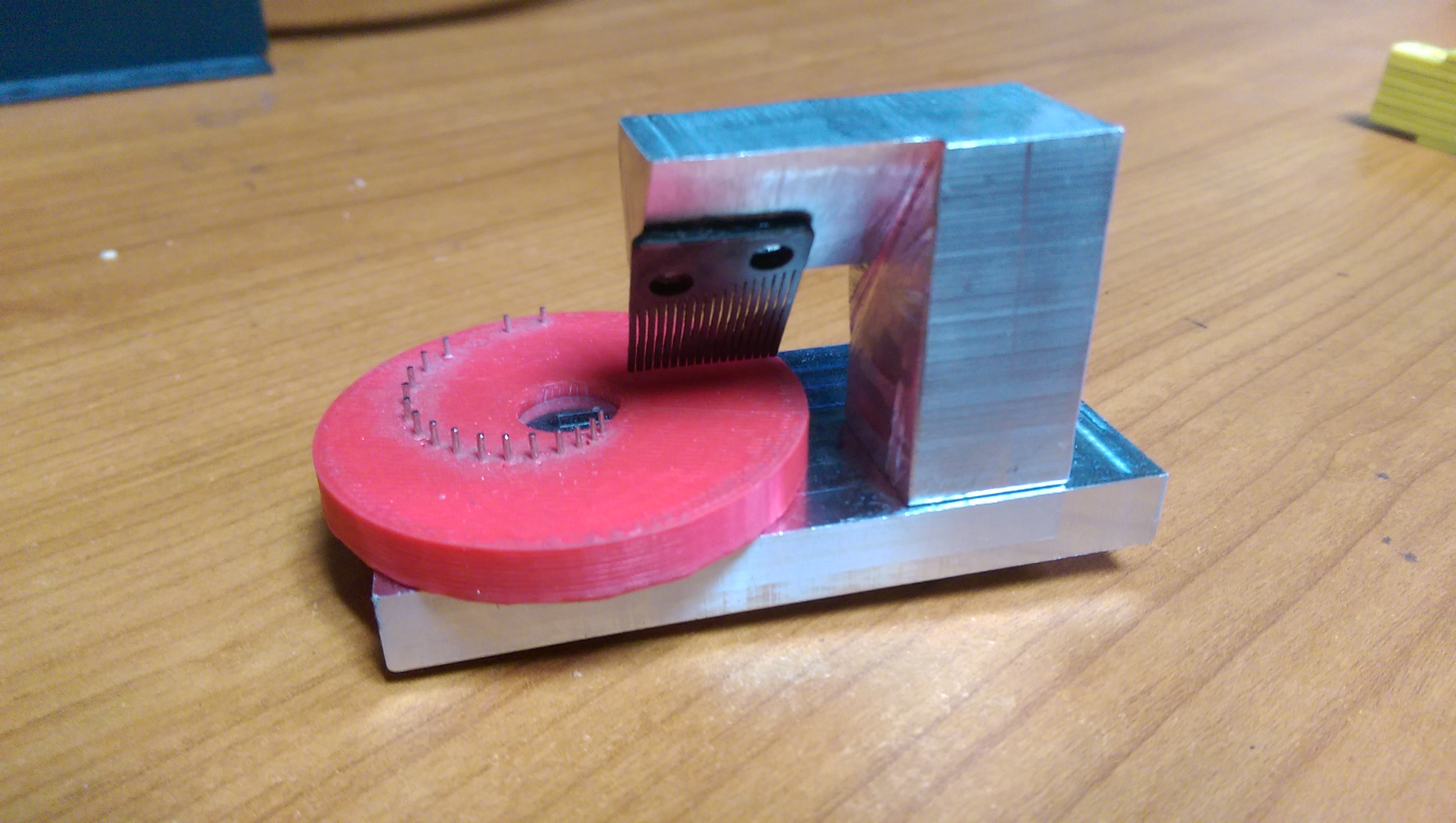
The first stage of the project is designing a note storage aspect which can be printed on a 3D printer. This design constraint meant that getting fine detail on the sides of an object would be very difficult, to avoid this a record style part was developed. This record would spin around on a base and pluck the teeth of the comb which would be suspended above.
This first piece which needed to be decided upon was the comb, all other dimensions depended upon it. The first attempt and subsequent research showed the level of detail and fine tuning necessary to be able to produce a comb which would give a good tone was out of the scope of this project. In order to advance, a comb was acquired and studied to understand the individual parts. From there, the design was altered in order to use the new comb.
With an overall design in place, fabrication began on the two structures which would hold the disk and comb. The base was the first piece produced and was machined out of aluminum. It consists of a peg which the record spins about and a mounting point for the arm to hold the comb. The arm was the next part with the square design seen in the CAD drawings. Subsequent testing saw better results with the comb on an angle, this resulted in the design being altered and reversed to accommodate. With the structure done, the focus was put on the disk. The first disk was produced entirely on a 3D printer this includes the pegs. The design flaw here is that because the pegs need to be rather small, they were very easily broken off. In order to remedy this a second prototype was developed which uses metal pins which are inserted after the print. This not only strengthens the pins, it also gives a more eloquent tone when played. This design, however, is more difficult to produce.
Project Files & Resources
General Resources
- Andrew Gregory Resources
WPI Student Contributors
2016
- Andrew Gregory